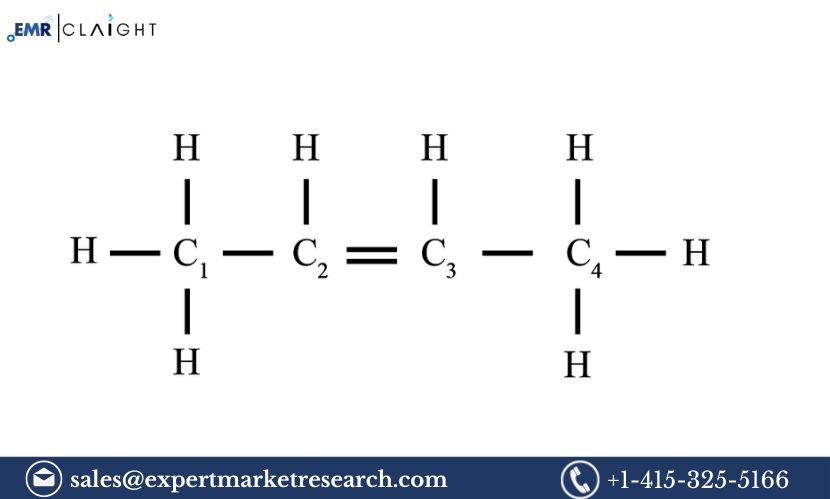
Introduction
Pentene is an important organic compound in the chemical industry, primarily used in the production of synthetic resins, plasticizers, detergents, and other industrial chemicals. As a member of the alkene family, pentene exists in several isomeric forms, such as 1-pentene, 2-pentene, and others. These variants have different applications depending on their structure and reactivity. The increasing demand for petrochemical products in industries such as packaging, automotive, and construction has led to the growing importance of pentene. This Pentene Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides a detailed analysis of setting up a pentene production facility, including raw material sourcing, production processes, machinery and equipment, market trends, financial considerations, and potential returns on investment.
Key Components
Setting up a Pentene Manufacturing Plant involves several critical steps, from sourcing raw materials to the final production and marketing of pentene products. Below are the key elements involved in establishing such a plant:
1. Raw Material Sourcing
The main feedstocks for pentene production are hydrocarbons, typically derived from crude oil and natural gas. These can be processed using various techniques to extract pentene. Key raw materials include:
- Crude Oil or Natural Gas: These sources provide the necessary hydrocarbons for cracking to produce ethylene, propylene, and pentene.
- Catalysts: High-efficiency catalysts are required in processes like catalytic cracking and polymerization to ensure maximum yield of pentene.
A reliable supply of these raw materials is essential for continuous plant operation. Ensuring a consistent and affordable supply of crude oil or natural gas is crucial for minimizing production costs.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
2. Manufacturing Process
The production of pentene typically involves the following processes:
-
Cracking: The primary method for producing pentene is catalytic cracking, where larger hydrocarbons (e.g., ethane, propane, or butane) are broken down into smaller molecules like pentene. This can occur in either a steam cracking or fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) unit.
-
Isomerization: In some cases, pentene is produced by the isomerization of lighter alkenes like butenes or hexenes, which are modified using catalysts to form pentene.
-
Purification and Separation: After cracking and isomerization, the pentene must be purified. This can involve distillation, membrane separation, or adsorption methods to remove impurities such as unreacted hydrocarbons, water, or other by-products.
3. Machinery and Equipment
Setting up a pentene manufacturing plant requires a variety of equipment for different stages of the production process. Some essential machinery includes:
- Cracking Furnaces: These are used for thermal or catalytic cracking to break down the raw hydrocarbons into smaller molecules, including pentene.
- Reactor Units: Reactors are used in the isomerization process, where catalysts facilitate the rearrangement of hydrocarbons to produce pentene.
- Distillation Columns: Distillation units separate the different fractions of hydrocarbons, ensuring that the pentene is purified and collected effectively.
- Compression and Storage Units: These systems are required to store the liquid pentene under controlled conditions before it is sent to the packaging or downstream processing units.
4. Energy Requirements
Energy is a major component of the operating costs for a pentene manufacturing plant. The cracking process, in particular, requires high temperatures, and the plant will need a reliable power supply. Energy-efficient designs, such as cogeneration plants or the use of waste heat recovery systems, can help optimize energy consumption and reduce costs.
5. Environmental Considerations
The production of pentene, like other petrochemical processes, can have significant environmental impacts, including air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation. To comply with environmental regulations and sustainability goals, the plant must integrate the following:
- Emission Control Systems: Technologies such as scrubbers, filters, and catalytic converters can be used to limit harmful emissions from cracking furnaces and other stages of production.
- Waste Management: Proper disposal and treatment of by-products such as unreacted hydrocarbons, water, and solid residues are crucial for reducing environmental harm.
- Water Recycling: As water is used extensively in cooling and other stages, implementing water recycling systems can reduce the plant's water consumption and waste discharge.
6. Market Trends and Opportunities
The market for pentene has grown steadily in recent years, driven by the demand for plastics, resins, and synthetic rubber. The key factors influencing the pentene market include:
- Increasing Demand for Plasticizers: Pentene is used as a precursor for manufacturing plasticizers, which are in high demand in the production of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and other plastics.
- Automotive and Construction Industries: Pentene is used in the production of synthetic rubber, which has applications in tires, seals, and various automotive components.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Growing environmental concerns are driving the demand for sustainable and energy-efficient processes in the petrochemical industry, presenting opportunities for advancements in pentene production technologies.
7. Investment and Financial Considerations
Establishing a pentene manufacturing plant involves significant capital investment. Some of the main costs to consider include:
- Land and Infrastructure: Purchasing land and constructing the necessary buildings and facilities.
- Machinery and Equipment: High-capital investments are required for purchasing cracking furnaces, distillation columns, reactors, and other equipment.
- Raw Materials: Continuous procurement of feedstock such as crude oil or natural gas is essential for uninterrupted plant operation.
- Operating Expenses: Ongoing costs such as labor, utilities, and maintenance are critical to ensure the plant runs smoothly and profitably.
- Environmental Compliance: Implementing necessary emission control measures and waste management systems requires investment in technologies and regulatory certifications.
8. Revenue Potential
The revenue potential for a pentene manufacturing plant depends on several factors, including:
- Production Capacity: The size and scale of the plant, and its ability to meet market demand for pentene, directly influence revenue.
- Market Demand: The demand for pentene products in various sectors, including the plastics, automotive, and construction industries, plays a major role.
- Product Pricing: Prices for pentene fluctuate based on raw material costs, production efficiency, and global market conditions.
FAQ
1. What is pentene used for?
Pentene is used as a precursor in the production of synthetic resins, plasticizers, synthetic rubber, and other industrial chemicals.
2. What are the raw materials for producing pentene?
The primary raw materials are hydrocarbons derived from crude oil or natural gas.
3. How is pentene produced?
Pentene is produced by catalytic cracking of hydrocarbons or through the isomerization of lighter alkenes.
4. What equipment is required for a pentene manufacturing plant?
Key equipment includes cracking furnaces, reactors, distillation columns, and storage units.
5. Is pentene environmentally friendly?
While pentene production can have environmental impacts, proper emissions control and waste management systems can help mitigate these effects.
6. What industries use pentene?
Pentene is widely used in industries such as plastics, automotive, construction, and chemicals.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au